Fungal infections By: amin alajlouni. - ppt download
4.6 (84) · $ 13.50 · In stock
We can classify Fungal infections, into: 1- non-inflammatory: A. Tinea versicolour B. Tinea nigra C. Piedra 2- Inflammatory: A. Tinea Capitis B. Tinea cruris C. Tinea pedis D. Tinea Corporis E. Tinea Barbae F. Tinea Ungum
Fungal infections By: amin alajlouni
1- non-inflammatory: A. Tinea versicolour. B. Tinea nigra. C. Piedra. 2- Inflammatory: A. Tinea Capitis. B. Tinea cruris. C. Tinea pedis. D. Tinea Corporis. E. Tinea Barbae. F. Tinea Ungum.
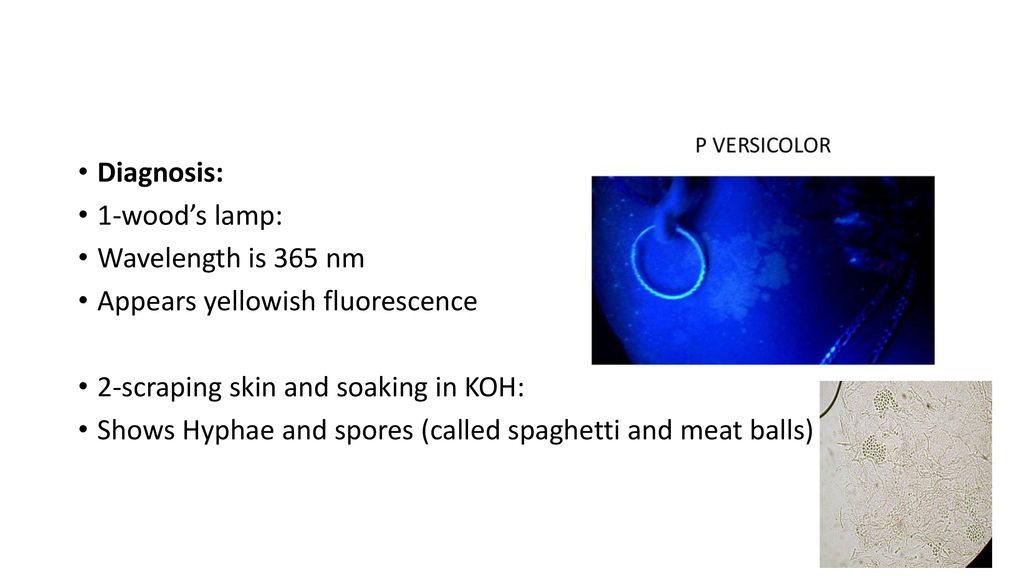
Tinea versicolor: Caused by Malassezia furfur (it is part of the normal flora) How does normal flora cause disease 1-increased humidity which allows more proliferation. 2-bad hygiene of the patient. 3-keeping in mind its lipophilic so doesn’t affect children (because their lipid profile isn’t well developed yet)
In areas where sebaceous glands are present (anterior chest, back, axilla, neck mainly)
Shows Hyphae and spores (called spaghetti and meat balls)
Treatment: Topical antifungals Or systemic antifungals if widespread
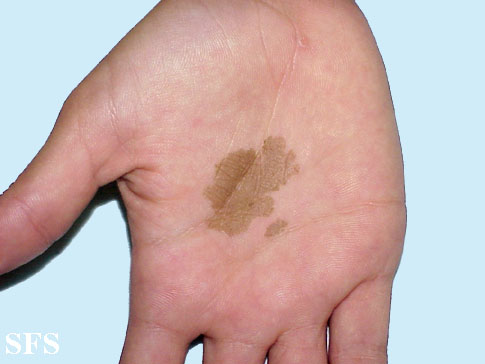
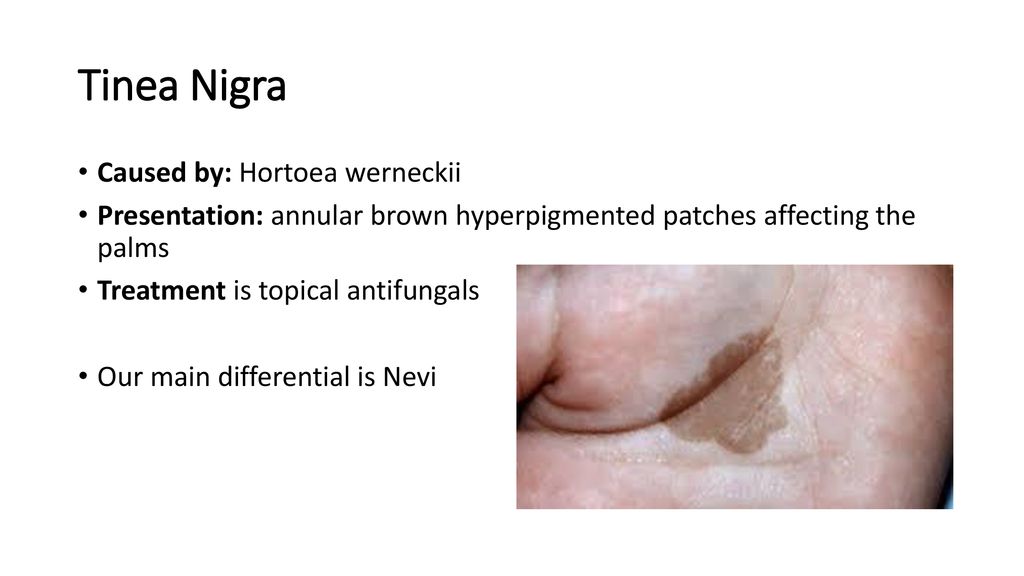
Presentation: annular brown hyperpigmented patches affecting the palms. Treatment is topical antifungals. Our main differential is Nevi.
White Piedra caused by: Trichosporan beigelii. Black Piedra caused by: Piedraia Hortae. Presents as: palpable yellow nodules on the hair shaft. Mainly associated with bad hygiene standards. Treatment: showering and antiseptics.
Some terminology: Capitis : scalp. Corporis: skin. Unguium: nails. Pedis: interdigital webspaces. Cruris: groin. Barbea: beard.
Caused by microsporum canis followed by M.audini. Outside the hair shaft. Diagnosed by KOH. wood’s positive apple green fluoroscents. 2-non-inflammatory: Caused by trichophytan tonsurans. Appears as black dots on affected areas which present as patchy hair loss. Diagnosis by KOH also. Wood’s negative. Both are treated with systemic antifungals.
Caused by trichophyton scheonleinii. Appearing on wood’s light as white to blue fluorescence. It is a dermatological emergency because permanent hair loss can occur with scarring or even sepsis. Kerion sign indicates severe inflammation.
Presents as annular erythematous scaly patches with pustules on rim and healing centers (ring warm of skin) Treated with topical antifungals.
Appears as an erythematous lesion with pustules and boggy appearance. Should be treated fast because of risk of scarring and hair loss. Treated with: Topical antifungals. Systemic antifungals. Antibiotics.
Divided into four types: 1- inter digital (4th and 5th spaces): most common type. presents as white macerated skin. common in diabetics. 2- inflammatory: Extends to soles and appears as vesicles or bullae. 3- ulcerative type. 4-Mucisin.
Except the inflammatory type most commonly caused by T.mentagrophyte only.
Also topical antifungals. Unless the patient is diabetic or immunosuppressed, we go with oral antifungals.
We here have 3 types: 1-distal and lateral type: which is most common. onycholysis with subungal hyperkeratosis. 2-superficial white. 3-proximal: in this subtype we have to rule out HIV. All are caused by T. rubrum most commonly. And all treated with systemic antifungals (2 months for finger nails, 3 months for toe nails)
Presents as: erythematous scaly pruritic patches affecting mainly the inner upper thigh and can extend to genitalia and buttocks. Risk factors: diabetics, pregnant, obese people. This disease is always compared to candida because they may present similarly.
4-angular stomatitis in candida (also contact dermatitis, iron and b12 def.) Also think of risk factors for candida: 1- HIV 2- immunosuppression. 3- antibiotic abuse 4-intra nasal or oral steroids.
A LOT OF WAYS!!! 1- oral thrush. 2- in flexures (bright red with satellite lesions) 3- anal cleft. 4- vulvovaginitis. 5-ring and middle finger. 6-paronychia. 7-chronic mucocutanous candidiasis.

Fungal rhinosinusitis

IJERPH January-2 2022 - Browse Articles
Sustainability June 2018 - Browse Articles

ACADEMIC JOURNAL

PDF) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy identifies heavy metal arsenic(V)-mediated enhancing effect on antibiotic resistance
Fungal infections By: amin alajlouni. - ppt download

Fungal infections By: amin alajlouni. - ppt download

PDF) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy identifies heavy metal arsenic(V)-mediated enhancing effect on antibiotic resistance

IJERPH January-2 2022 - Browse Articles

Sustainability June 2018 - Browse Articles

Fungal infections By: amin alajlouni. - ppt download

PDF) AJHS 383
Fungal infections By: amin alajlouni. - ppt download